Automated Laundry Management System
Samsung Software Membership
Automated Laundry Management System
Samsung Software Membership · Mar 2016 - May 2016
TL;DR
Role: System and Embedded, Android (team of 3)
Stack: WPF (.NET), Arduino, Bluetooth, Raspberry Pi 2 with Pi Cam, PHP, Android
What it does: Unmanned laundry system that integrates membership and payment, power control, and live remaining-time
Impact: Device sync errors reduced from about 15% to below 2%, 30+ fault-free demo cycles, relay misfire 0 cases
Outcome: Presented at SSM final seminar as a complete end-to-end prototype
Problem
Unmanned laundry shops often lack integration among payment, power control, and remaining-time tracking.
Users cannot see accurate status, owners cannot control machines reliably, and devices desync under load.
My Role
- Designed the PC–Arduino–Android communication protocol over Bluetooth and TCP
- Built a WPF dashboard for live status and control, plus state and log views for owners
- Implemented a Raspberry Pi capture pipeline for remaining-time snapshots and server upload
- Developed the Android client for remote monitoring and push alerts
Solution Highlights
1) Reliable Bluetooth serial
Backoff-based reconnect, sequence id with CRC, and idempotent commands for safe retries
2) Stable timer reading
Fixed ROI and pre-processing with morphology and threshold, N-vote consensus for ±5 s accuracy
3) Deterministic control flow
State machine with Idle, Armed, Running, Locked states to prevent race conditions and double triggers
Results
- 30+ consecutive runs without faults in demo conditions
- Power relay misfires 0 cases, remaining-time error within ±5 s
- Owners can see per-machine status and logs, users receive push alerts when their laundry is done
Demo and Architecture
Hardware
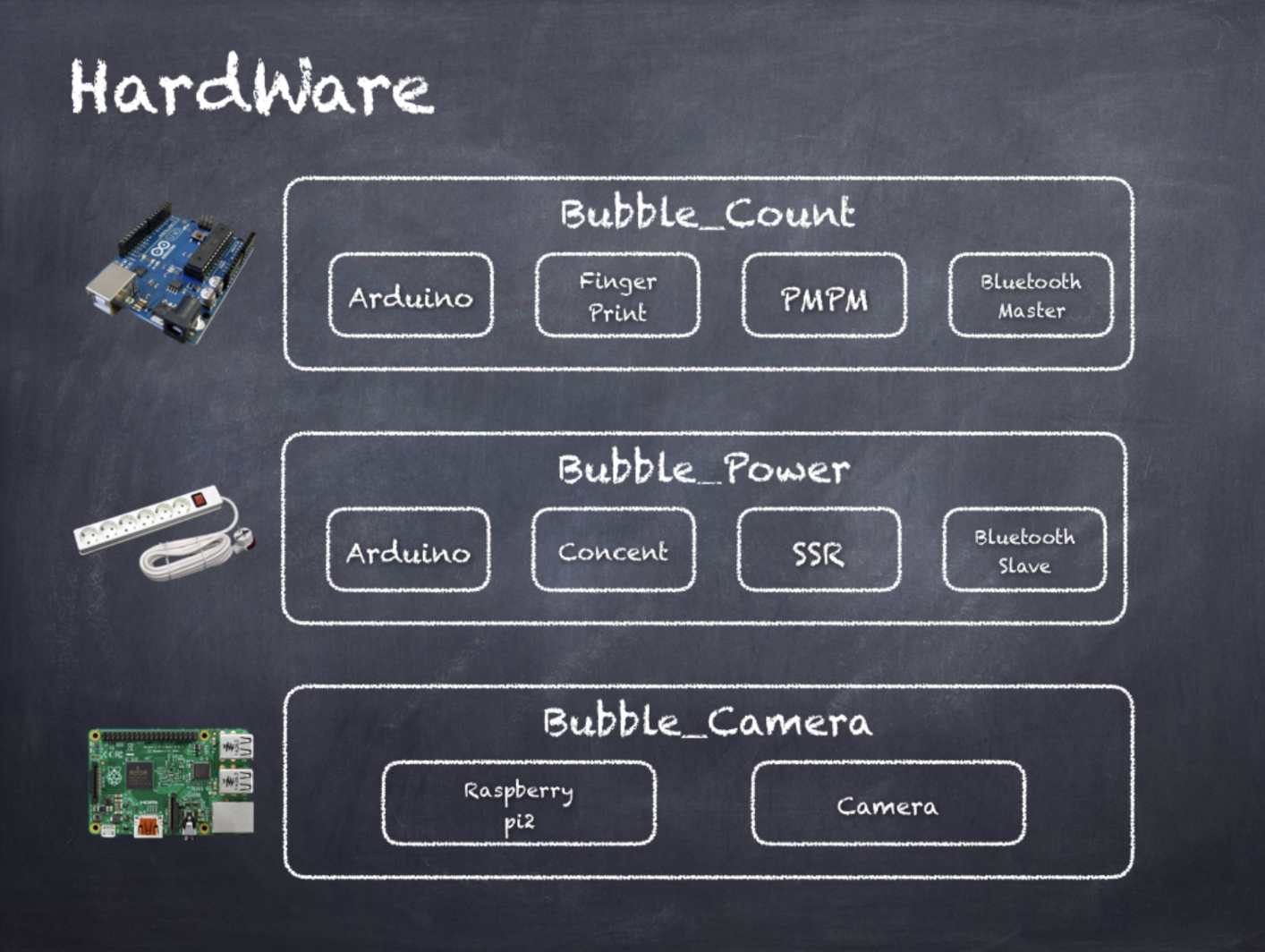
- Bubble Count: Arduino for bill acceptor and fingerprint, sends values via Bluetooth
- Bubble Power: Arduino and SSR for safe on and off control
- Bubble Camera: Raspberry Pi 2 with Pi Cam, sends processed snapshots to the server
Software
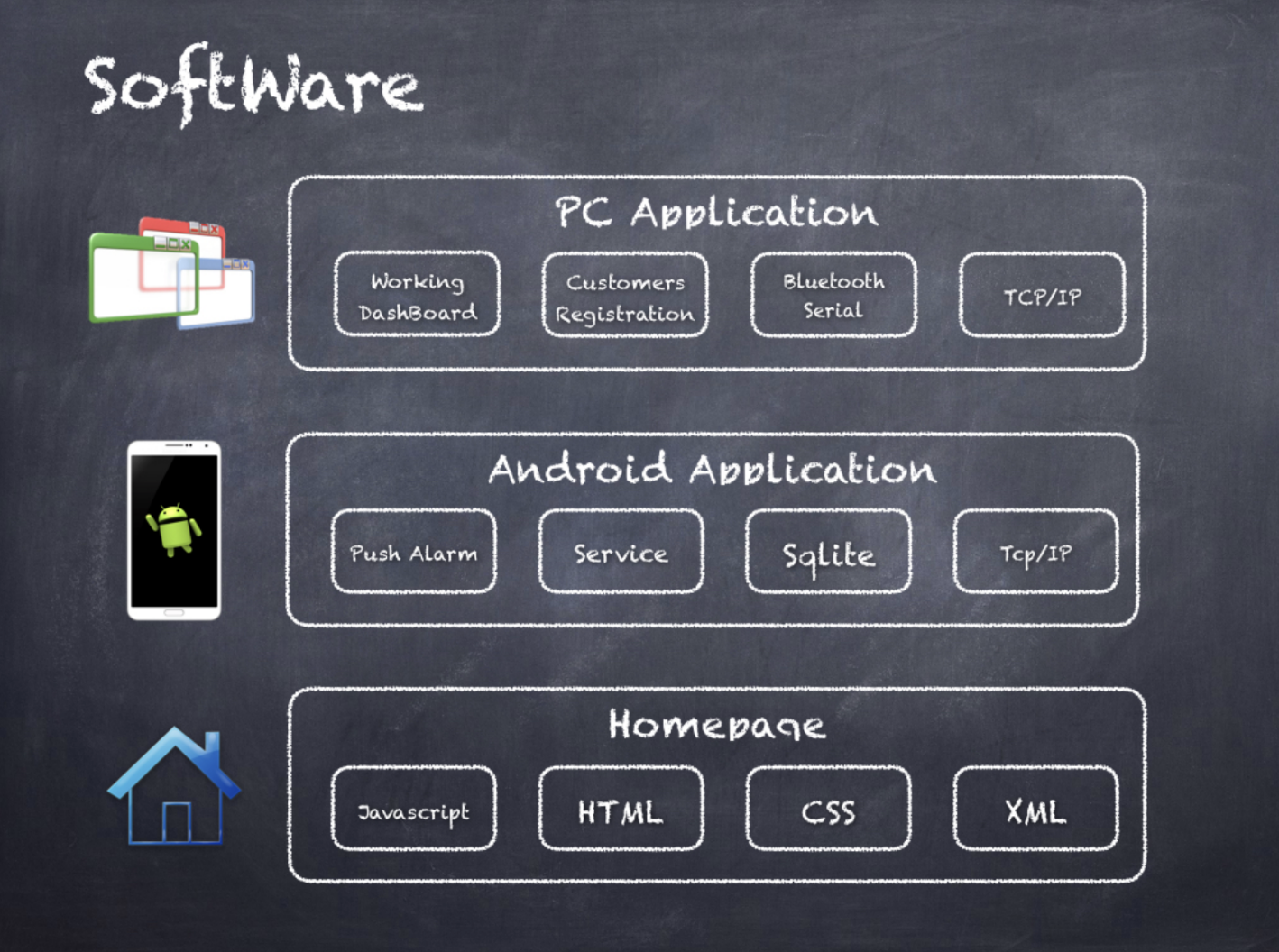
- PC app (WPF): Dashboard, membership handling, and machine control through Bluetooth and server
- Android app: Live status and push alerts, local encrypted SQLite for user data
- Server (PHP): Bridge between PC and Android, exposes facility and device status
Cost snapshot (KRW)
- Fingerprint reader: 79,000
- Bill acceptor: 79,000
- Arduino Nano × 2: 67,328
Total ≈ 229,028
View full budget table
| No | Part Name | Purpose | Price (KRW) | Quantity | Total (KRW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SSR (Solid State Relay 240VAC 15A with housing) | Washing machine on and off | 1,000 | 1 | 1,000 |
| 2 | O-ring terminal | Power outlet | 1,700 | 1 | 1,700 |
| 3 | Grounding outlet | Power outlet | 1,000 | 1 | 1,000 |
| 4 | Arduino Nano | Hardware MCU | 33,664 | 2 | 67,328 |
| 5 | Fingerprint reader | Membership management | 79,000 | 1 | 79,000 |
| 6 | Bill acceptor | Membership coin handling | 79,000 | 1 | 79,000 |
| Total | 229,028 |
Technical notes
WPF, IoT, Arduino, OpenCV, Bluetooth, PHP
- WPF: XAML and data binding for a real-time dashboard
- IoT and BLE: Single master design for stability within 10 m conditions
- OpenCV: Pre-processing with morphology and threshold, fixed ROI for robust reading
- Bluetooth: Sequence and CRC for packet checks, retry and reconnect logic
- PHP: Server bridge that exposes device and facility status to clients
Extras
Project duration and schedule
- Duration: 2016.03.06 – 2016.05.06
- Milestones:
- Kick-off: 2016.03.09
- Mid-term: 2016.04.20
- Completion: 2016.05.11
- Final submission: 2016.05.12
Images: environment, equipment



Résumé bullets
- Built end-to-end unmanned laundry system across PC, Arduino, and Android. Integrated payment, membership, power control, and live remaining-time.
- Designed Bluetooth protocol with retry and backoff, sequence and CRC, and idempotent commands. Reduced device sync errors from about 15% to below 2%.
- Implemented WPF dashboard and Raspberry Pi capture pipeline. Achieved 30+ fault-free demo cycles and push alerts for users.