PROJECTS
Wireless USB Adapter for Wired Devices
Samsung Software Membership
Wireless USB Adapter for Wired Devices
Samsung Software Membership
Summary
- Goal: Turn existing wired keyboards and mice into wireless devices via a dongle, without buying new peripherals.
- Approach: Two dongles per set (keyboard + mouse). Each dongle has battery, Bluetooth module, and USB host chip (VNC1L). Data is sent to a PC dongle (Atmega128 + V-USB) that appears as HID keyboard and mouse.
- Stack: C/C++, Qt (key-setting GUI), Linux device driver, AVR firmware. Zigbee was tried first; switched to Bluetooth for lower latency (Zigbee 30–50 ms was too slow for real-time input).
Project duration and environment
- Duration: 2014.10 – 2015.03
- OS: Linux Ubuntu 14.04 LTS, Windows 7
- Languages: C / C++
- Tools: Qt Creator, GCC, AVR Studio
Background & purpose
- Wired keyboards and mice are limited by cable length and placement; wireless versions cost more.
- This project adds a small adapter between existing wired devices and the PC so they work like wireless ones, using Bluetooth for low latency and reasonable cost.
System architecture
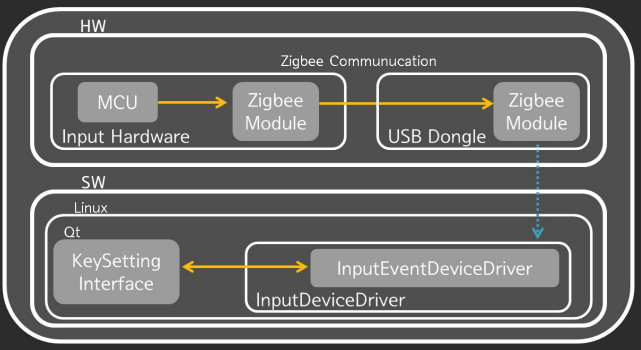
- Each input device (keyboard, mouse) has a dongle with an MCU.
- MCU sends input data to the PC dongle over Bluetooth.
- PC dongle runs firmware (V-USB) and is recognized as one HID keyboard and one HID mouse.
- Qt-based key-setting app lets users assign shortcut keys and map them to programs (Linux).
Hardware
PC dongle
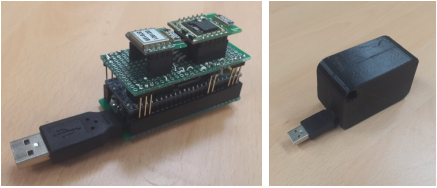
- Atmega128 as USB device (V-USB). Two Bluetooth modules receive data from keyboard and mouse dongles.
- PC sees one HID keyboard and one HID mouse. Case designed in CATIA and 3D-printed.
Mouse dongle

- VNC1L (FTDI) as USB host: reads USB mouse data and sends it to the PC dongle via UART + Bluetooth.
- Case: CATIA + 3D printer.
Keyboard dongle

- Same idea as mouse; VNC1L needs external AT commands for monitor mode, so an extra MCU is used to send those commands.
Assembly (concept)

- Keyboard and mouse each plug into their own dongle; portable battery powers them. PC dongle plugs into a USB port. Pairing takes about 5–10 seconds.
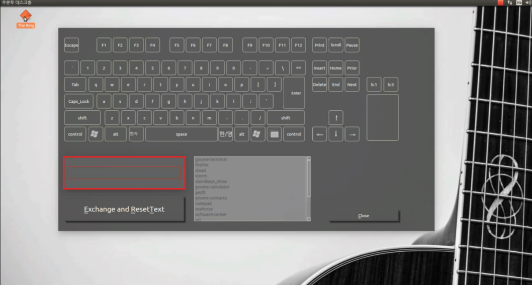
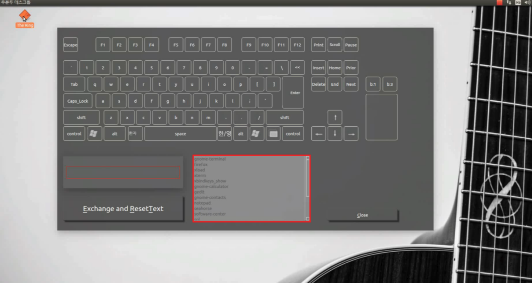
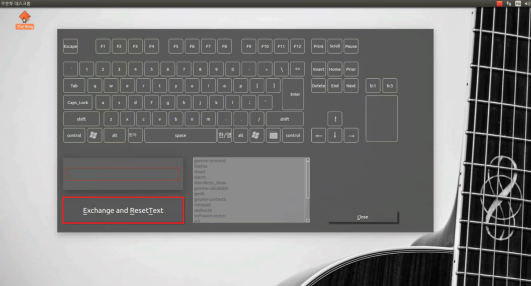
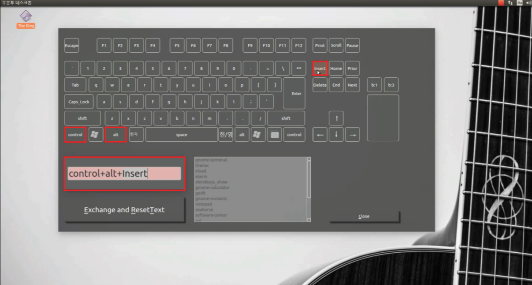
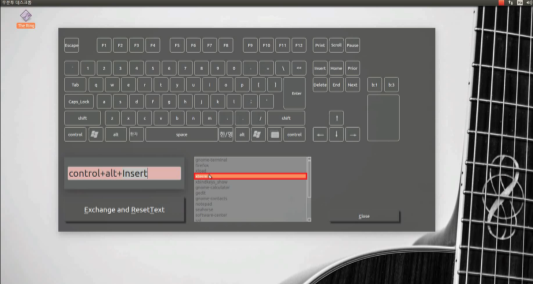
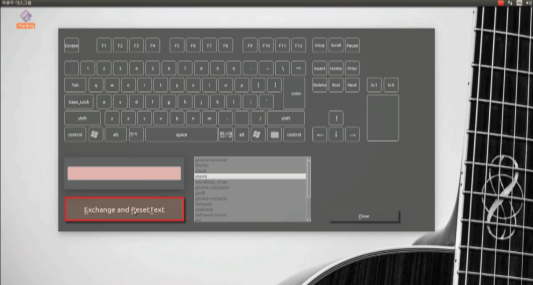
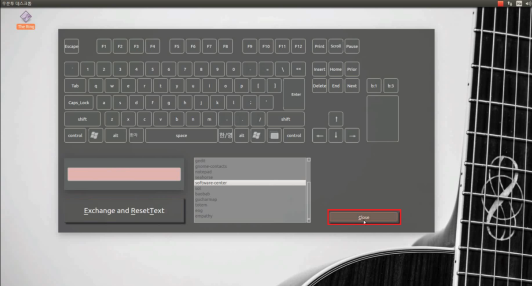
Software: key-setting interface (Qt)
- GUI built with Qt: virtual keyboard and mouse buttons; user composes key combinations and ties them to programs (e.g. shortcut to run an app).
- Flow: Click virtual keys → combination appears in a text area → choose a program from a list (or add one) → “Exchange and ResetText” saves the mapping and clears for the next one.
- Screenshots below: main window, combination builder, program list, and registered shortcuts.
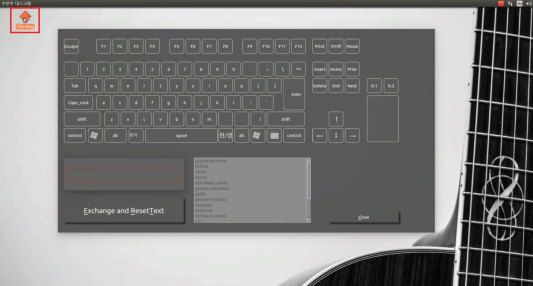
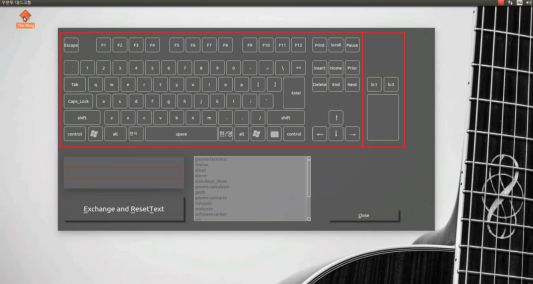
Development budget (KRW)
| No | Part Name | Purpose | Price (KRW) | Qty | Total (KRW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FZ755AC | Data transmission | 44,000 | 4 | 172,000 |
| 2 | VNC1L Board | USB host | 38,000 | 2 | 76,000 |